What are Vitamins?
Vitamins are micro-nutrients that we generally get through our diet that often act as enzymes and co-factors in metabolic reactions.
Properties of vitamins:
- Heat sensitive
- Different vitamins are soluble in fat or water
Vitamin A
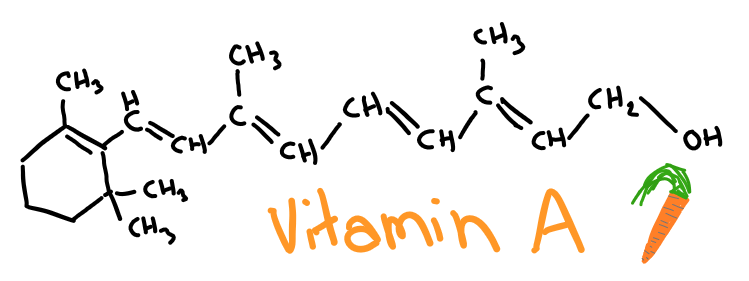
- Contains a conjugated double and single bond system
- Absorbs light giving vitamin A an orange colour
- Fat soluble
- Largely non polar
- Contains few H bonds
- Therefore not excreted in urine
- Found in carrots
, mangoes and sweet potatoes
- Stored in the liver and fatty tissues
- Used mainly in vision and sight
Deficiency
- Called Nycatalopia or night blindness
- Reduces sight (basically you can’t see)
Vitamin C
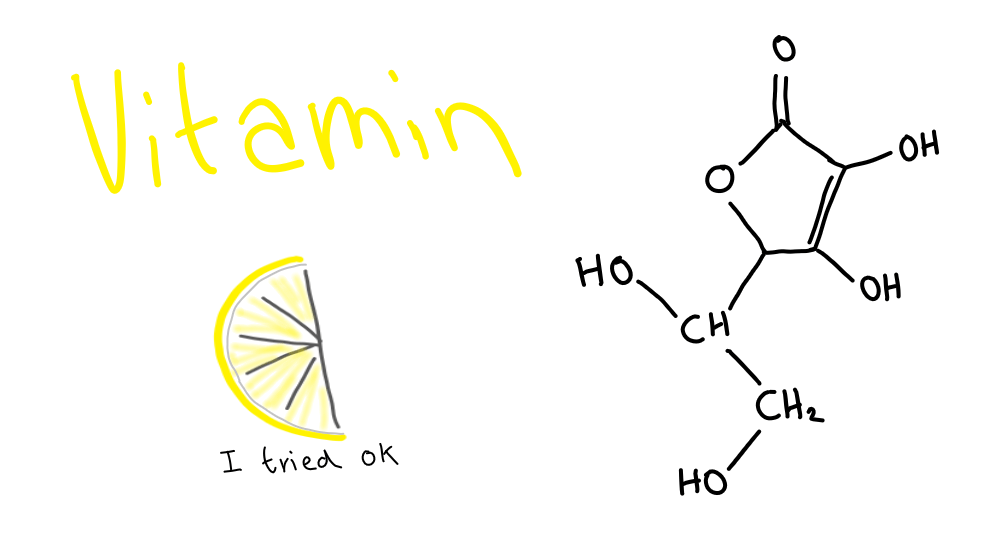
- Water soluble
- Contains many polar groups and hydrogen bonds
- Excess Vit. C is excreted in the urine.
- Found in citrus fruits e.g. oranges, lemons, limes etc.
- Used as an antioxidant
- Quenches reactions involving free radicals
- Acts as a reducing agent by giving electrons to free radicals
- Quenches reactions involving free radicals
- Used to maintain general health and prevent scurvy
Deficiency
Vitamin C deficiency, called scurvy, causes gum disease, weakness and fatigue. It occurred frequently in sailors back in the day on long distance travels as they were unable to store fresh citrus fruits.
Vitamin D

- Fat soluble
- Mainly non-polar
- Synthesised in the skin from cholesterol in a reaction catalysed by light
- Used to help absorb microminerals such as calcium, zinc and magnesium
Deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency or rickets causes soft and weak bones as well as stunted growth.
Tackling Vitamin Deficiency
Vitamin deficiency often occurs due to malnutrition in developing nations. Preventative measure include:
- Providing diverse vegetables and foods
- Eating plenty of fruit and vegetables (eat your peas?!?!)
- Maintaining a balanced diet
